Recent Findings: July 27, 2020
Recent Findings: July 27, 2020
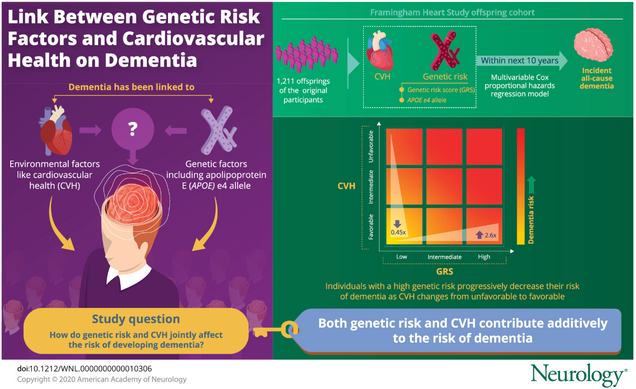
Image Credit: © 2020 American Academy of Neurology
Dementia-associated common gene variants or the APOE e4 genotype can more than double dementia risk, but good cardiovascular health can decrease dementia risk by 50%, according to a study published in Neurology by FHS investigators. Researchers from Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) and School of Medicine (BUSM) noted that because these effects are additive, genes and cardiovascular health can independently add to or subtract from a person’s risk of developing dementia.
According to the study authors, those with high genetic risk of dementia can still lower their risk by adopting a healthier lifestyle. For this study, researchers scored participants on the American Heart Association’s seven components of cardiovascular health: physical activity, cholesterol, healthy diet, blood pressure, weight, blood glucose, and smoking status.
The research team found that participants with a favorable cardiovascular health score were 55 percent less likely to develop dementia than participants with an unfavorable score.
Per Medical News Today:
“We hope that the results of this study will send the public a message, and that message is to exercise, reduce stress, and eat a healthy diet. Then, regardless of your genes, you have the potential to lower your risk of dementia.” – Dr. Sudha Seshadri
The team noted that the study was limited by its small sample size, and the fact that the Framingham Heart Study is composed of individuals of European descent. This means that results may not be generalizable to non-European populations. Additionally, some of the genetic markers may influence both cardiovascular health and dementia.
In conclusion, “In a community-based sample, we observed that both genetic risk and cardiovascular health are additively associated with incident dementia. Further studies are needed to replicate these results in larger as well as ethnically diverse samples.”
Read article full text online: